Question:
Explain binary code, ASCII, and Unicode.
Answer:
Binary Code
- Definition:
- Binary code is a system of representing data using only two digits: 0 and 1. It is the fundamental language of computers and digital communication.
- Bits and Bytes:
- A binary digit is called a bit. Eight bits form a byte, which is the basic unit of storage in computers.
- Data Representation:
- Computers use binary code internally to represent all types of data, including numbers, text, images, and instructions.
- Binary Arithmetic:
- Binary code is essential for performing arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, etc.) in computers through logic gates that process binary data.
- Machine Language:
- Computer processors execute instructions represented in binary code, known as machine language, directly.
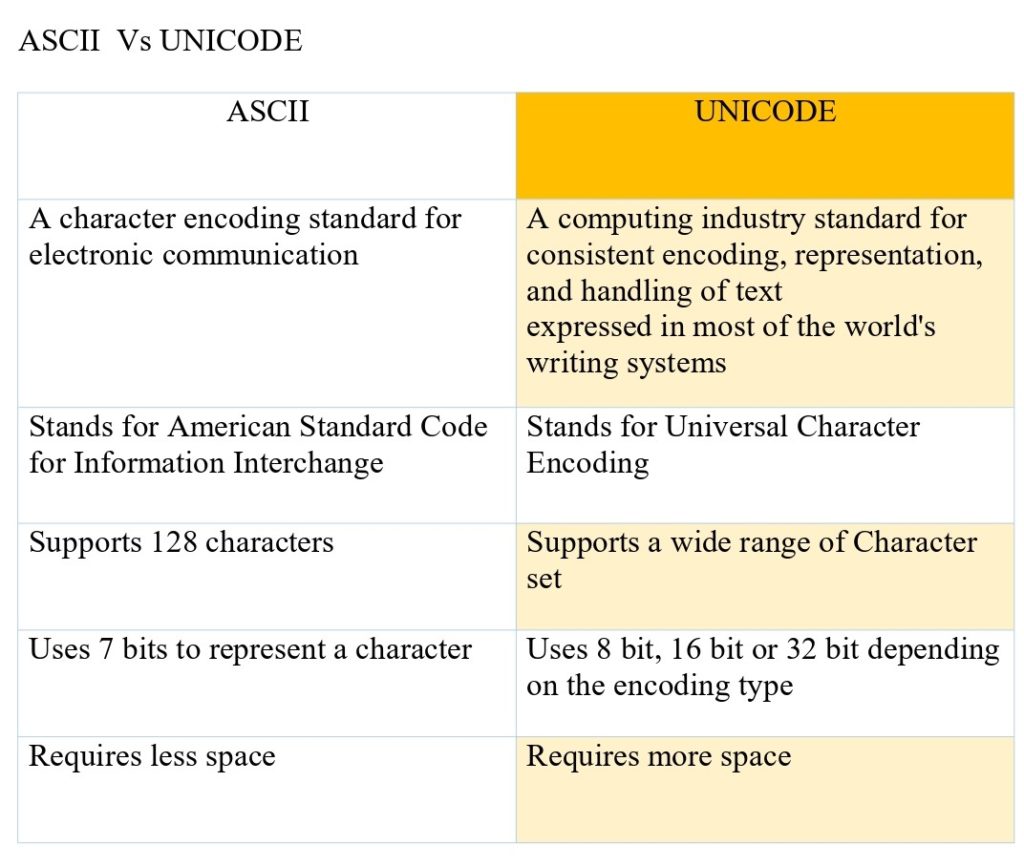
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange)
- Character Encoding:
- ASCII is a character encoding standard originally developed for teletype machines in the early days of computing.
- Character Set:
- It defines a set of 128 characters, including control characters (like newline and tab) and printable characters (letters, digits, punctuation).
- 7-Bit Representation:
- Each ASCII character is represented by a 7-bit binary number (0 to 127). Later extended versions (such as Extended ASCII) used 8 bits to accommodate more characters.
- Universal Standard:
- ASCII became widely adopted as a universal standard for encoding text in English and other Western languages in early computer systems.
- Limitations:
- ASCII only supports characters from Western European languages and lacks support for characters in other scripts (like Chinese, Arabic).
Unicode
- Definition:
- Unicode is a character encoding standard designed to support the global representation of text and symbols across different languages and scripts.
- Expansion from ASCII:
- Unicode builds upon ASCII by providing a unique numeric code (code point) for every character, including characters from non-Western scripts, emojis, symbols, and special characters.
- Multilingual Support:
- It supports over a million code points, allowing representation of characters from all major languages worldwide, historical scripts, mathematical symbols, and more.
- UTF-8 Encoding:
- UTF-8 is a popular encoding scheme for Unicode that uses variable byte lengths (1 to 4 bytes per character) to efficiently represent all Unicode characters.
- Standardization:
- Unicode is widely adopted in modern computing, ensuring consistency in text representation across different platforms, applications, and devices.
In summary, binary code is the foundation of digital data, ASCII is an early standard for text encoding in computers primarily for Western languages, and Unicode is a comprehensive standard supporting global text representation across languages and scripts.